Science Writing #1 Universe
| |||||||
Universe Size and Scale -- Know Your Galactic Address
On the board Comprehending the size of the universe is incredibly difficult. This project will help you understand the vastness of space Gloop Glork, a friend in a distant galaxy wants to send you a letter about her trip to a black hole. A regular address has only three or four lines. Due to the great distance, the address has to be specific so the letter can get to you. PROCEDURE:
|
| ||||||||||||
Universe is History
Talk to your neighbor for 1 minute and answer these:
•Where would astronomers need to look to find galaxies in their earliest stages of life (babies)? •Where would we find galaxies in their later stages (senior citizens)? |
Light Travel Times |
The universe is weird, expanding, and explained by the Big Bang Theory

Students took guided notes on the Big Bang Theory.
Strong lines of evidence include:
|
Expanding Universe Outline
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation |
| ||||||||
http://history.cpet.ufl.edu/siftguide/astro.htm
Ballooniverse |
Outline Alternatives
| ||||||
Warping of Space
A new set of breathtaking photos reveals a never-before-seen deep view of the universe.
Released as the first "Frontier Fields" view from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, the new images mark the deepest-ever observations of a cluster of galaxies. The photos center on Abell 2744, a group of several hundred galaxies 3.5 billion light-years away from Earth.
The images also capture background galaxies more than 12 billion light-years away, whose light has been magnified and brightened by the immense gravity of Abell 2744 in a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, researchers said.
http://www.nasa.gov/content/hubble-frontier-field-abell-2744/#.UtAdEft0nKc
Released as the first "Frontier Fields" view from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, the new images mark the deepest-ever observations of a cluster of galaxies. The photos center on Abell 2744, a group of several hundred galaxies 3.5 billion light-years away from Earth.
The images also capture background galaxies more than 12 billion light-years away, whose light has been magnified and brightened by the immense gravity of Abell 2744 in a phenomenon known as gravitational lensing, researchers said.
http://www.nasa.gov/content/hubble-frontier-field-abell-2744/#.UtAdEft0nKc
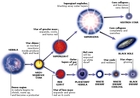
Timeline of the Universe
|
Something you should try- http://www.johnkyrk.com/evolution.html. It’s a timeline from the big bang up to the Protozoic Era. The animations are eye catching, and it’s a breeze to use. Loading times may be slow due to all of the different pictures you’ll see, but it’s well worth it. Credit goes to John Kyrk.
|
Galaxy Types
|
Galaxies Outline
Vocabulary
| ||||||||||||||||||
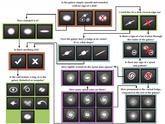
Galaxy Classification Practice
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
Galaxy Type Practice #1
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
Galaxy Type Practice Option #2
|
The following website is needed for the classifying galaxies for today's activity:
http://cse.ssl.berkeley.edu/SegwayEd/lessons/classifying_galaxies/student1.htm |
Universe and Galaxy Reading Passage
|
| create-your-own-galaxy-project.doc | |
| File Size: | 43 kb |
| File Type: | doc |

Students completed a viewing guide on galaxies
How the Universe Works - Galaxies (part 1 of 3)
How the Universe Works - Galaxies (part 2 of 3)
How the Universe Works - Galaxies (part 3 of 3)
In this episode scientists talk about the estimated 200 billion galaxies in the known Universe and explains where galaxies came from, how they work, what's their future and how they will die.
How the Universe Works - Galaxies (part 1 of 3)
How the Universe Works - Galaxies (part 2 of 3)
How the Universe Works - Galaxies (part 3 of 3)
In this episode scientists talk about the estimated 200 billion galaxies in the known Universe and explains where galaxies came from, how they work, what's their future and how they will die.
Universe and Galaxies Quiz Part 2 Review
Intro to Star Life Cycles
Star Life Cycle Reading Passage
|
|
Star Guided Outline #1 Star Birth
| star_life_cycle_guided_outline_one.doc | |
| File Size: | 30 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
| star_life_cycle_part_one.ppt | |
| File Size: | 7790 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
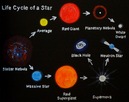
Star Life Cycle Diagram

Click to see this
beautiful star cluster
beautiful star cluster
- Content: Explore the evolution and life cycle of medium and large mass stars.
- Language Purpose: Use scientific vocabulary terms such as stellar, protostar, nebula, black hole, red giant, supernova, and white dwarf.
- Outcome: Work with shoulder partner to create a graphic organizer, differentiating the life cycles of medium mass and large mass stars.
Star Life Cycle Diagram Day Two
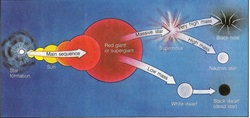
Student creates a diagram illustrating the life cycle of massive and average sized stars.
Descriptions of stages are added today |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Death of a Star | ||||||

Nuclear Fusion
|
| ||||||
Cosmos--Sisters of the Sun
|
Sisters of the Sun
Students take guided notes from the new Cosmos series. Notes deal with star life cycles. Notable stars featured: The Pleiades cluster, Eta Carinae, and Rigel. |
| ||||||
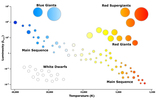
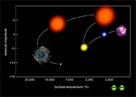
HR Diagrams
Learning Targets
|
|
Stars can be arranged according to their luminosity and temperature on a diagram. The current age and evolutionary state of a particular star can be determined by using this diagram.
Activity sheet contains two activities:
|
InteractiveWe have animated the HR diagram to help you understand how a star changes throughout its life. In this animation, a star will move throughout the diagram. DO NOT BE DECEIVED! The star does not physically zip around the universe as it ages. The star physically stays in the same location, but the movement is to show how luminosity (brightness) and surface temperature change with star age. Remember, it’s a diagram, not a star map. Stars and Personality? Is astrology a science or pseudoscience?We read and discussed a Relatively Interesting article on astrology.
Students predicted what the world would be like if astrology were What would the world be like if it did work?

Do horoscopes really all just say the same thing? 22,000 horoscopes were analyzed with an online tool called TagCrowd to find the most common words. The data we used to create a meta-chart or graphic. Analysis revealed that the bulk of the words in horoscopes (at least 90%) were actually the same. In fact the most common words could be combined to write a generic prediction.
Challenge Question: What are some characteristics indicating something may be pseudoscience? Stars Presentation
Nuclear Fusion
What would happen if the sun explodes?
Common student question: What would happen if the sun exploded?
The good news is that our Sun will never explode (even though more massive stars can and do). The Sun is big for a star, but just isn't massive enough to fuse anything past helium in its core. More massive stars can continue nuclear fusion until they make the element iron. This creates an unstable core which will then explode in a supernova explosion. So what would happen if our sun did somehow manage to explode? Go to this link and read this article.
Learn why these items are not threats to the world - or are they?: Alignment Polar Shift Supernova Volcanoes Solar Storms In the movie 2012 there were 2 times that they had to fly their plane fast to escape being destroyed. Play this game and see if you can pilot your way out of harm. After an alien attack the world is now an unfriendly place. You will have an armored suit and must defend against aliens and robots in Robot Rampage Another favorite is Bullethead Or maybe you could be Obama and defend the world against aliens in Obama Alien Defense
Atom Review
Subatomic Particles
Atomic Structure Diagram
Why do we need to do this cloud stuff?
Find someone who....
How Building Blocks Are There In The Universe?
Elements (about 114 right now known)
Counting Atoms Practice
Elements, Atoms, Compounds, and Molecules
Atom Element and Molecule PracticeTee Shirt Art
Design artwork for a tee shirt representing the differences between atom, element, molecules, and compounds. 1. Front of the shirt must have artwork (minimum of 4 colors) showing the concept above. 2. Back of the shirt must have a 1 or 2 line 'cute or clever (but clean)' saying using the concept above. 3. A minimum of 2 paragraphs explaining how the artwork and saying get the Chemistry idea across must be written. Song or Rap 1. The song must use the words atom, element, molecule, compound, and mixture. Remember: when presenting the song, be prepared to sing/play it out loud. 2. There must be an illustration (4 colors minimum) showing an understanding of the assigned vocabulary. 3. There must be a 2 to 3 paragraph explanation after the song and illustration to explain how each covers and demonstrates the assigned vocabulary. Create a Venn diagram representing the differences and similarities between atom, element, molecules, and compounds Periodic Table Practice
2/13/14 Periodic Table Practice #1
2/19/14 Periodic Trend Practice
2/27/14 Elements in Living Things
How are isotopes different?
2/26/14 Periodic Sentences
Famous Elements
Hunting the Elements
Organic vs Inorganic Chemistry
In Class Clicker Review
Periodic Table Quiz Review
You can review some online materials by clicking here.
Learning Targets
(Objectives) Level 3 1.Explain the relationship between position and motion 2.Compare and contrast speed and velocity 3.Explain how velocity is an example of a vector 4.Describe the relationship between velocity and acceleration 5.Describe the relationship between velocity and momentum 6.Interpret and create various graphs dealing with distance or velocity and time
Speed and Velocity Foldable
Speed Practice Problems
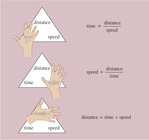
Reference Frames
Acceleration Triangle
Modeling Acceleration
Mass Versus Weight and Misconceptions About Falling Objects

Acceleration Problem Practice
Challenge Question: Josh rolled a bowling ball down a lane in 2.5 s. The ball traveled at a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2 down the lane and was traveling at a speed of 7.6 m/s by the time it reached the pins at the end of the lane. How fast was the ball going when it left Tim’s hand?
Acceleration Problems Practice Two
Is Antigravity and Levitation Possible?
Find Someone Who Can....Motion Review
Anti gravity Illustration
Acceleration on the human body
Common Accelerations
Force Diagrams
Force Practice Problems
Newton's Webquest Review
Find Someone Who Can.....Forces Review
Challenge # 2 Ladder Egg Drop
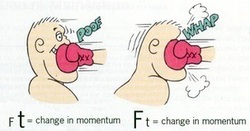
Momentum and Impulse
Which material would you prefer to have attached to your feet if you jumped off a building?
_
Sky Diver
· On the top half of the page:
Create an illustration that shows what forces are acting on a sky diver in free fall. Make sure to include force vectors. · On the bottom half of the page: Write a paragraph explaining the situation using academic vocabulary. Explain what forces are acting on the sky diver. Are the forces balanced or unbalanced? What is happening to the speed of the sky diver when they first jump out of the plane, when they are in free fall, and when they deploy their parachute? http://w3.shorecrest.org/~Lisa_Peck/Physics/syllabus/mechanics/momentum/eggdrop/eggdrop.html#parameters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||